Why Mine Data?
Everyone and everything is leaving a digital footprint.
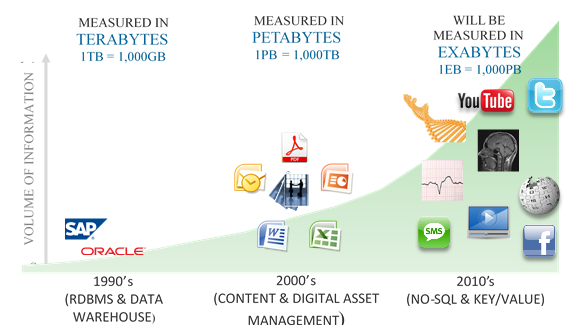
Lots of data is being collected and stored at enormous speeds (GB/hour). These data come from multiple sources, including:
• Medical Information, such as genomic sequencing and MRIs
• Increased use of broadband on the Web – including the 2 billion photos each month that Facebook users currently upload as well as the innumerable videos uploaded to YouTube and other multimedia sites
• Video surveillance
• Increased global use of mobile devices – the torrent of texting is not likely to cease
• Smart devices – sensor-based collection of information from smart electric grids, smart buildings and many other public and industry infrastructure
• Non-traditional IT devices – including the use of RFID readers, GPS navigation systems, and seismic processing
• Web data, e-commerce
• purchases at department/grocery stores
• Bank/Credit Card transactions
Data mining helps the company provide better, customized services for an edge or competitive advantage (e.g. in Customer Relationship Management). There is often information “hidden” in the data that is not readily evident. Human analysts may take weeks to discover useful information.
Data Mining is extraction of interesting (non-trivial, implicit, previously unknown and potentially useful) information or patterns from data in large databases.
What is not Data Mining?
– Look up phone number in phone directory
– Query a Web search engine for information about “Amazon”
– Calculate the differences in quarterly sales of tours between this year and the previous two years.
What is Data Mining?
– Group together similar documents returned by search engine according to their context (e.g. Amazon rainforest, Amazon.com,)
– From the customer purchase history, build a model for predicting the kinds of customer who are likely to purchase tours to a certain country